Category: Practical
-
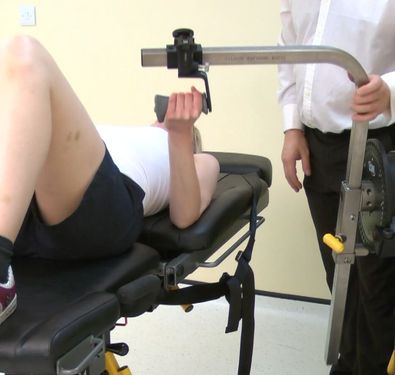
Elbow Flexion / Extension
These movements can be performed in either the standing, seated or lying (most popular position). Most movements around the elbow in everyday life, and in fact sport, occur with the hand free in space (open chain). The position of the elbow joint moves in space in relation to the shoulder which makes the two joints co-dependant. The action…
-
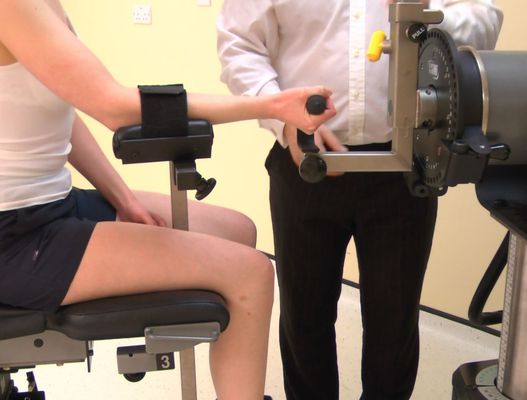
Elbow Pronation / Supination
There are currently no standard examination positions for pronation and supination. During these movements the shoulder is difficult to fully stabilize without using 90 degrees of shoulder abduction and even then the subject can move the shoulder somewhat the elbow is usually flexed to 90 degrees during these tests (as described by Gallager et al…
-
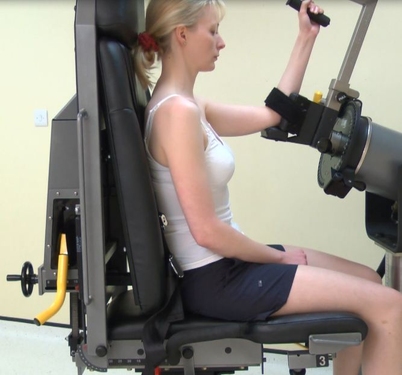
Shoulder Rotation
In recent years the most popular isokinetic test in the shoulder has been internal/ externalrotation (with modified seated in the scapular plane being the most popular). The main reason this test has become so popular is the open chain nature of shoulder motions. Most movements around the shoulder in everyday life, and in fact sport,…
-
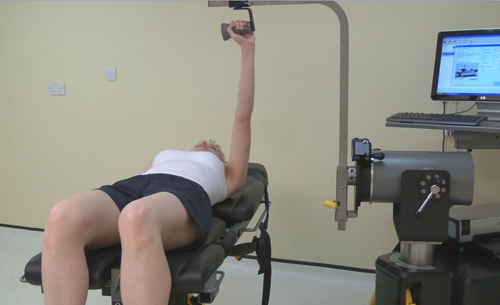
Shoulder Flexion / Extension
There are currently no standard examination positions for flexion and extension of the shoulder. During the movements of the gleno-humeral joint there are always relative movements within the scapulo-thoracic junction. These are usually described as fitting a set of established normal patterns. These must be considered when testing the shoulder. When testing or exercising the shoulder…
-
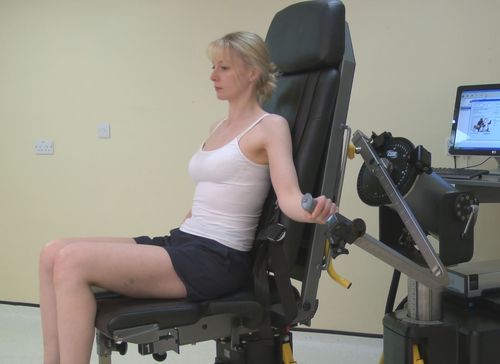
Shoulder Abduction / Adduction
These movements can be performed in either the standing or seated positions. There are currently no standard examination positions for abduction and adduction of the shoulder. During the movements of the gleno-humeral joint there are always relative movements within the scapulo-thoracic junction. These are usually described as fitting a set of established normal patterns. These must be considered…
-
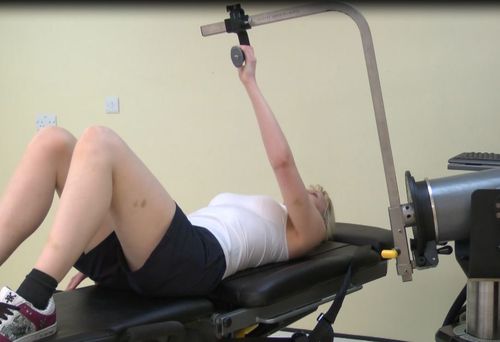
Shoulder Diagonals
There are two main diagonal patterns available on isokinetic machines. They mimic the proprioceptive neuromuscular patterns (PNF). The two movements are: PNF 1: Extension / abduction / external rotation to flexion / adduction / internal rotation PNF 2: Flexion / abduction / external rotation to extension / adduction / internal rotation These movements can be performed in either…
-
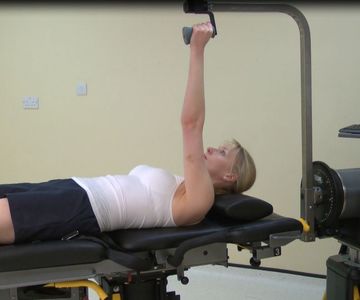
Shoulder Horizontal Abduction / Adduction
These movements can be performed in either the lying or seated positions. There are currently no standard examination positions for horizontal abduction and adduction of the shoulder. During the movements of the gleno-humeral joint there are always relative movements within the scapulo-thoracic junction. These are usually described as fitting a set of established normalpatterns. These must be considered when…
-
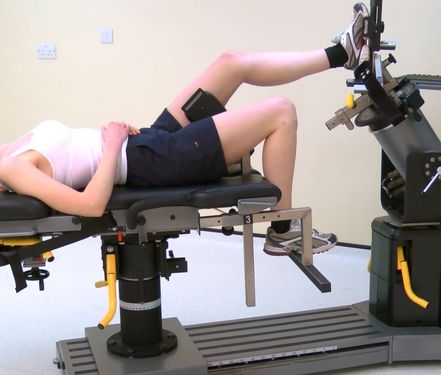
Internal / External Rotation
Internal and external rotation of the knee is a popular test especially in ski-ing populations. The popliteus and hamstrings muscles play a significant role in rotating the knee (internally and externally) to aid unlocking and locking the knee. It should be noted that this position stretches the ligaments at t the rear of the knee…
-
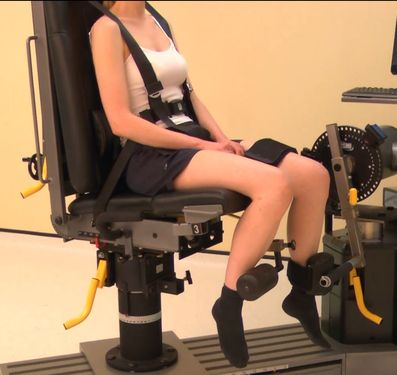
Knee Flexion / Extension
Until the late 1970s 75% of all isokinetic use and research was based on a single joint system – the knee. With more recent progress in rehabilitation and knee surgery this trend no longer exists. The basic design of isokinetic dynamometers (except for special purpose units) has not changed since the original instrumentation became available…